WunderQuiz
Faces of Philosophy : The Pre-Socratics

Faces of Philosophy : The Pre-Socratics
The quiz "Faces of the Philosophers: The Presocratics" lets you discover the early Greek philosophers who laid the foundations of rational thought before Socrates. Learn about Thales, Anaximander, Heraclitus, Pythagoras and other pioneers who explored the nature of the universe, fundamental elements and logic. This quiz helps you understand their contributions to philosophy, science and their innovative worldviews, offering insight into their ideas that have profoundly influenced Western thought.
Quiz Preview
Philosopher who lived around 624-546 BCE
Known for: water as substance, mathematics.
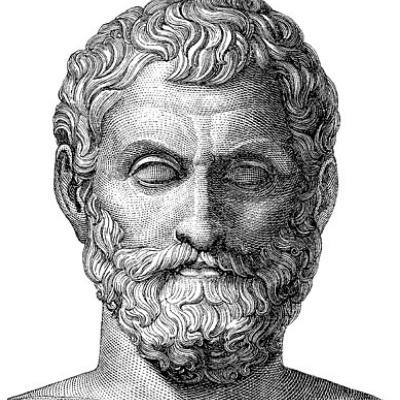

Often called the first Western philosopher, Thales proposed that the underlying principle (or archê) of everything is water.
He introduced a rational approach to understanding the cosmos, moving away from purely mythological explanations.
Philosopher who lived circa 610-546 BCE
Known for: his scientific methods. The original principle is ἀπειρον / ápeiron ("unlimited").
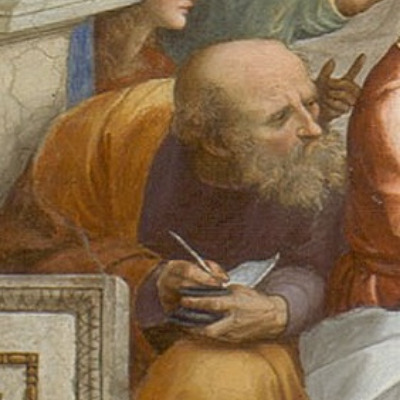

A student of Thales, Anaximander introduced the concept of the "apeiron" (the boundless or indefinite) as the source of all things. He also made significant contributions to early cosmology and geography.
Philosopher who lived around 585-525 BCE
Known for: Air as a primary substance
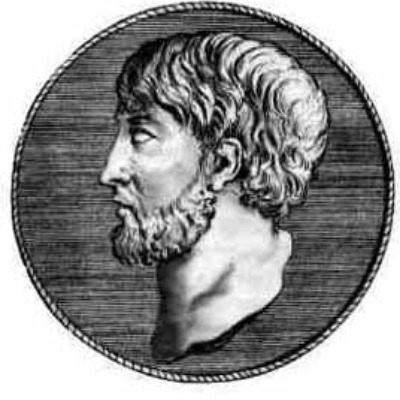

Another Milesian philosopher, Anaximenes proposed air as the primary substance, suggesting that different states of air (through condensation and rarefaction) could explain the diversity of the world.
Philosopher and religious reformer who lived around 570-495 BCE
Known for: vegetarianism, mathematics, harmony of the spheres
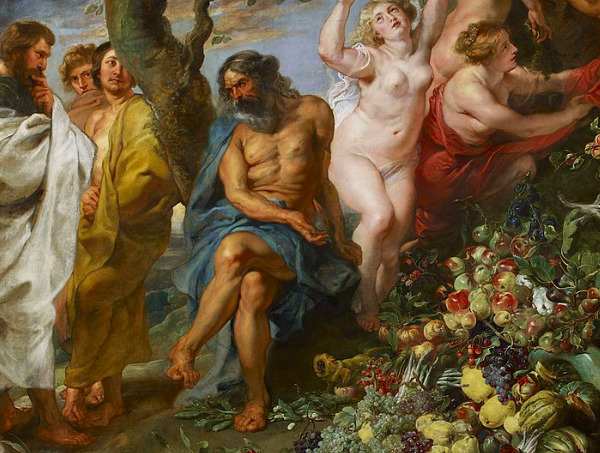

Known for his mathematical and philosophical teachings, Pythagoras believed in the transmigration of souls and the harmonious structure of the universe, often represented through numerical relationships.
Philosopher who lived around 570 - 475 BCE
Known for: abandoning polytheism and the anthropomorphic conception of the gods.

Xenophanes critiqued the anthropomorphic depictions of gods in Greek poetry and religion, arguing for a more abstract and singular conception of the divine.
He also contributed to early discussions on epistemology, suggesting that human knowledge is fallible and that certainty is ultimately unattainable.
Philosopher who lived around 535-475 BCE
Known for: the union of opposites, Cosmic Dynamism (panta rhei)

Famous for his doctrine of flux, Heraclitus argued that everything is in a state of constant change. His fragment "No man ever steps in the same river twice" encapsulates this idea.
Philosopher who lived around 510-560 BCE
Known for: the introduction of logic, being and non-being
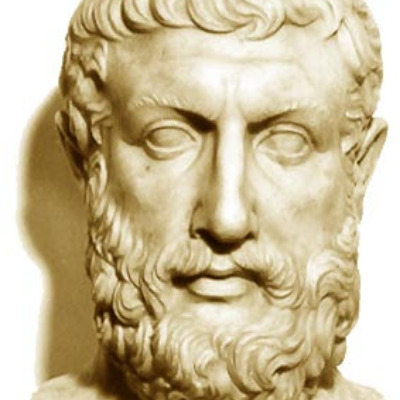

Parmenides is known for his poem "On Nature," which presents a monistic view of reality, arguing that change and plurality are illusions. His ideas significantly influenced later philosophers, including Plato.
Philosopher who lived around 500-428 BCE
Known for: concept of "noûs" (νοῦς), a kind of spirit, director of the world. Theory of the Moon's reflection.

Known for his theory of "homoeomeries," Anaxagoras argued that everything contains a portion of everything else. He also introduced the concept of "nous" (mind) as the ordering principle of the universe.
Philosopher who lived around 492 -420 BCE
Known for: religious agnosticism, relativism.
"Man is the measure of all things."
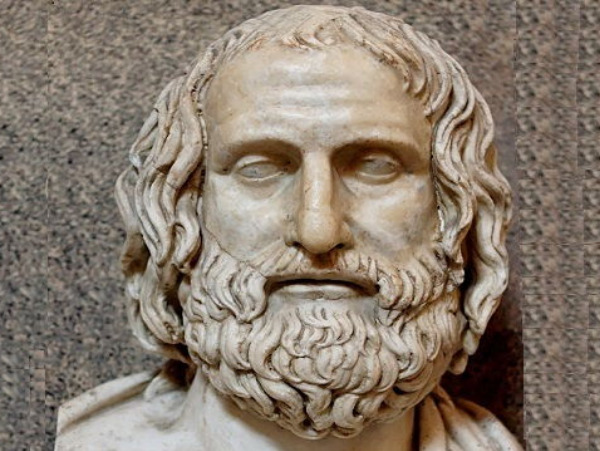

Protagoras is famous for his relativistic maxim, "Man is the measure of all things," which suggests that knowledge is subjective and relative to the individual.
As a Sophist, Protagoras was known for teaching rhetoric and virtue, and he was one of the first professional educators in ancient Greece.
Philosopher who lived around 490-430 BCE
Known for: paradoxes of movement and dialectics.

A student of Parmenides, Zeno is famous for his paradoxes, which were designed to support Parmenides' monism by showing the absurdities that arise from assuming the reality of motion and plurality.
Philosopher who lived around 490-430 BCE
Known for: two cyclical principles of the universe, Love and Hate. Four elements: water, earth, fire and ether.

Empedocles proposed the four classical elements (earth, air, fire, and water) as the fundamental substances, along with the forces of love and strife that cause them to mix and separate.
Philosopher who lived around 460-370 BCE
Considered the inventor of philosophical atomism.

Leucippus is often credited, along with his student Democritus, for the development of atomism, the theory that the universe is composed of tiny, indivisible, and indestructible particles called atoms.
Philosopher who lived around 460-370 BCE
Disciple of Leucippus. Considered a materialist, the universe is made up of atoms and vacuum.
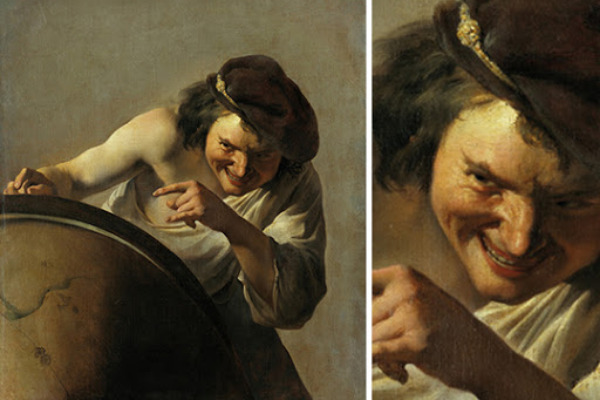

Along with his teacher Leucippus, Democritus is credited with the development of atomism, the idea that the universe is composed of indivisible and indestructible particles called atoms.